India Is Using AI and Satellites to Map Urban Heat Vulnerability Down to the Building Level
India Is Using AI and Satellites to Map Urban Heat Vulnerability Down to the Building Level
In a groundbreaking initiative, India is harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI)…
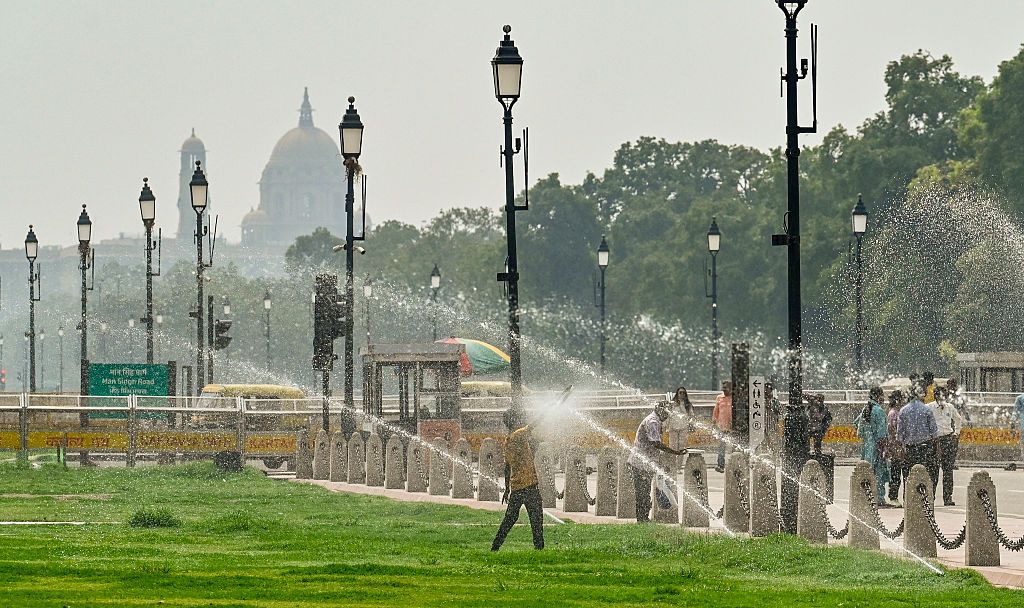

India Is Using AI and Satellites to Map Urban Heat Vulnerability Down to the Building Level
In a groundbreaking initiative, India is harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and satellite technology to map urban heat vulnerability at a granular level, down to individual buildings.
This innovative approach is allowing policymakers and city planners to identify areas that are most at risk of extreme heat conditions, and to develop targeted strategies for mitigating the impact of rising temperatures.
The use of AI and satellite data is providing unprecedented insights into the complex relationship between urban development, climate change, and heat vulnerability.
By analyzing factors such as building materials, land use patterns, and tree canopy coverage, researchers are able to pinpoint specific areas where heat is likely to be most intense, and where vulnerable populations may be at higher risk.
This data-driven approach is helping to inform decision-making processes around urban planning, infrastructure development, and public health policies, with the goal of creating more resilient and sustainable cities.
By mapping heat vulnerability at such a detailed level, India is leading the way in using cutting-edge technology to address the urgent challenge of urban heat islands, which disproportionately affect low-income communities and marginalized populations.
The insights generated from this mapping project have the potential to transform how cities around the world address the growing threat of extreme heat, and to create more climate-resilient urban environments for all residents.
As climate change continues to exacerbate heat-related risks, the use of AI and satellite technology to map urban heat vulnerability down to the building level represents a critical step towards building more sustainable and equitable cities for the future.